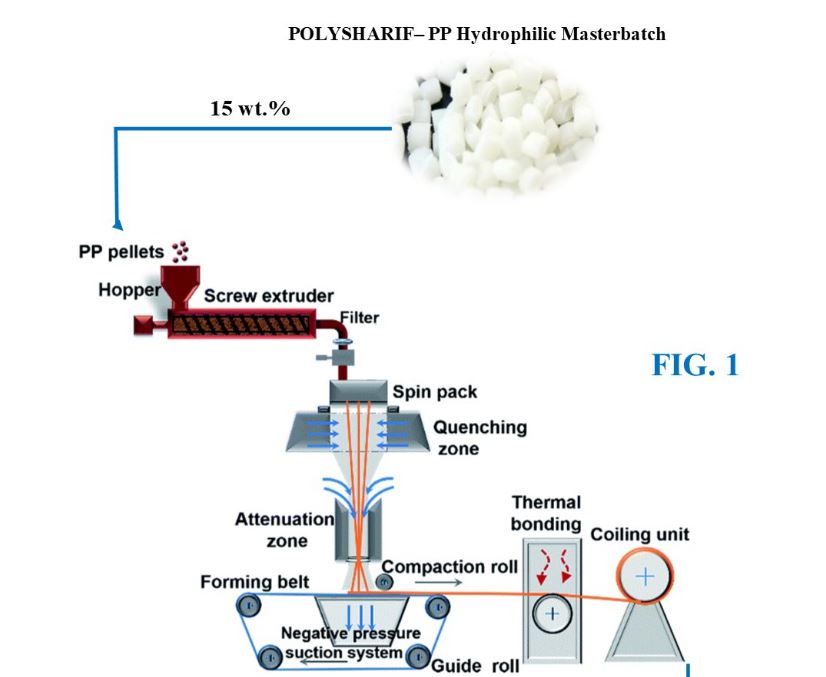
Polysharif-Hydrophill Masterbatch can be employed in textile industries. This masterbatch can be utilized in Spunbond and Spunlace products and make them hydrophilic. The base of the masterbatch can be any thermoplastic polymers including polypropylene, polyester and etc.
The hydrophil masterbatch is added during the melt processing of the final product fabrics in the range of 10 to 15 wt.%, depends on the application and type of the products. The hydrophilic properties of the fabric can be induced immediately after the manufacturing process or a few hours after the process (less than 24 hrs).
It’s worth to state that the hydrophilic properties caused by this masterbatch is permanent and can not be de-stroyed after washing the products. The masterbatch is FDA approved and does not make any human skin sen-sitivity.
Polypropylene (PP) fibers, widely utilized in nonwoven industry, have highly hydrophobic surface properties. Therefore, a modification in order to create a polar surface is an important issue where wettability and adhesion properties are required.
PP has a very low value of the surface free energy and, consequently, has very weak hydrophilic properties. In many industrial applications there is a need to modify the polymer surface with keeping their desired unchanged bulk properties. Chemical treatment of the surfaces is the most often used method for inducing, hydrophilicity. In conventional methods, the produced nonwoven fabric will be impregnated via specific solution passing through a bath and subsequent drying and rolling. The hydrophilic properties induced by this method is temporary, costly and may make smell during water absorption.
However, the economical-technical requirements, force the industry to search alternative efficient methods. The surface energy and the polar contribution of the polypropylene film increased due to the migration of low-molecular-mass components (additives) to the surface resulting in increase in surface wettability. Our experiments reveals migration and surface enrichment of additives via concentration difference between the surface and the core of the fiber. In addition, a more hydrophilic surface will be made by increase in the surface amount of polar oxygen groups.

What they do to make hydrophilic PP spunbond?
Their special way to impart surface hydrophilicity into polypropylene is blending of the melt additives during the fiber spinning process. In fact, the hydrophilic masterbatch, containing ologomeric additives, is added during the melt processing of the final product fabrics in the range of 10 to 15 wt.%, depends on the application and type of the products. The hydrophilic properties of the fabric can be induced immediately after the manufacturing process (FIG. 1).
According to their researches, oligomeric additives, spun with host polymer, migrate to surface and generate surface hydrophilicity at low concentration without altering bulk properties. The additives migrate to the surface gradually leading to a durable hydrophilic PP surface.
More about all this in categorie RAW MATERIAL - subcategory Chemicals - Resins - To enter in contact with them click on Price or Sample request !

1192